DarkNet – a hidden network where connections are made only between trusted peers, sometimes called friends, using non-standard protocols and ports. An anonymous network is a system of unbound virtual tunnels that provide encrypted data transmission.
Darknet has earned a reputation as a sinister abyss, an “underground” associated with criminal activity. And there are reasons for that because many crimes in the world that are deeply rooted in the Darknet.
You cannot access the DarkNet through a standard browser (Google Chrome, Safari, etc.) – this requires special encryption software, such as the browser Tor. The privacy provided by TOR creates an environment in which criminals can sell their products and services without having to worry about complying with the law.
When we hear spooky stories about stealing funds from bank accounts or identity theft, the question is how easy it is to get someone else’s personal information, documents, etc.
The answer to this question was given by Privacyaffairs specialists, who carried out research on the Internet and published the following data.
PLAY-BY-PLAY
There are a lot of trading platforms on the DarkNet, but even more forums with messages warning of fraudsters. These made it difficult to get the real price without ordering goods and services.
The researchers’ methodology was to monitor various marketplaces, forums, and websites and to create an average price index for several specific products.
The focus was only on products and services related to personal data, fake documents, and social networks.
CREDIT CARD DATA
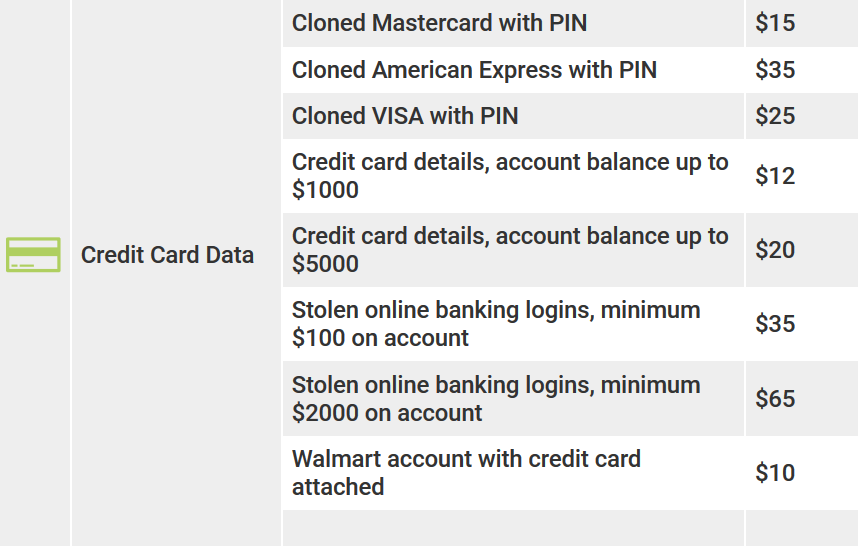
Credit card data usually provided in this format:
|EMAIL|PHONECC|MM|ADDRESS_|CITY|YY|PHONE|EMAILCC|MM
where the first four fields are the data of the card itself, and the remaining fields are the information about the cardholder.
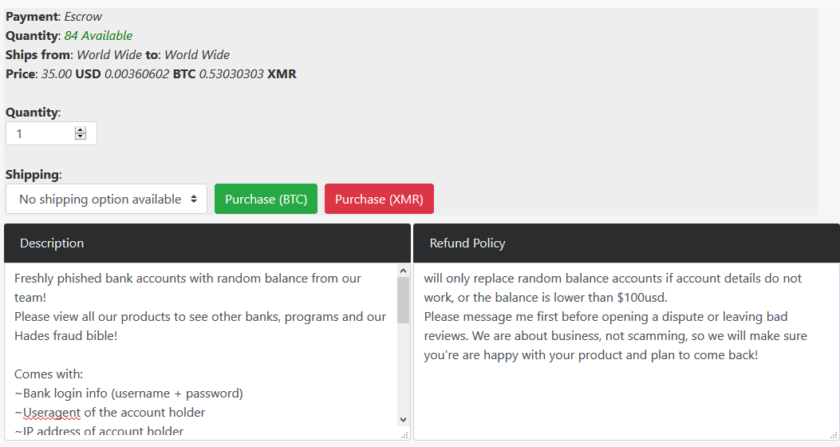
Sellers usually give an 80% guarantee. That means that two out of ten cards will not work, or they will have a balance less than the one declared.
Specialists at Privacyaffairs did not order anything, so they could not check whether this is true, but this statement is justified because there are more and more cases of fraud with identity falsification. These indicate a high level of turnover of such data.
PAYMENT PROCESSING SERVICES
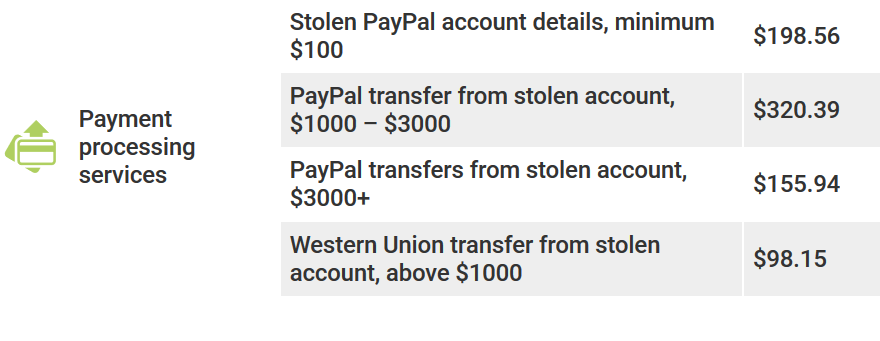
During the survey period, PayPal account data was the most common and very cheap. Real transfers from a hacked account were more expensive.
Another common selling point was manuals on how to cash-out money – getting money by avoiding the law. These manuals cost a few cents, but we have no idea if they work because they were not in the research focus.
FORGED DOCUMENTS
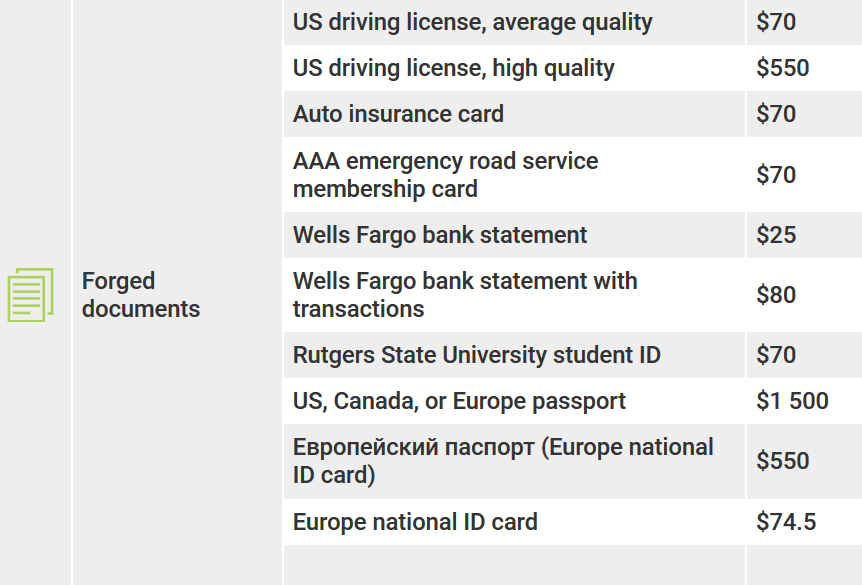
Such documents are provided with some guarantees and with any details required by the purchaser. With only a little real information about someone, a criminal can create a range of official documents that can be used for all types of fraudulent activities. That is the case when an identity has been stolen.
COUNTERFEIT MONEY
Fake banknotes are extremely common, mostly in denominations of 20 or 50.
Often researchers have encountered US dollars, euros, British pounds, Canadian and Australian dollars. Some come with a guarantee of ultraviolet inspection. The price of quality, as a rule, is about 30% of the value of the banknote.
SOCIAL MEDIA
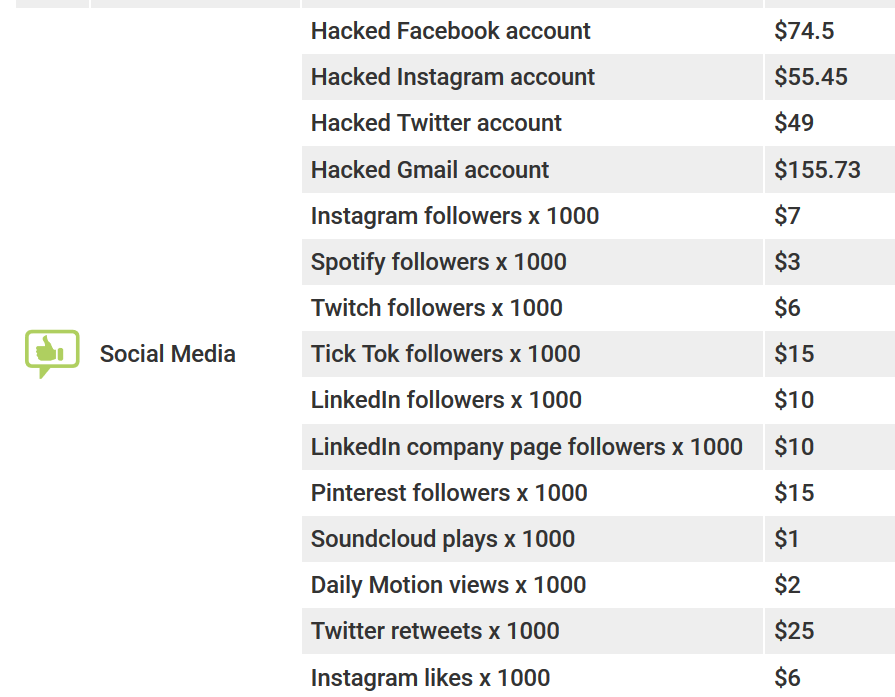
Suggestions to hack into accounts or sell them were relatively rare, but it doesn’t mean that they do not exist. These may be due to a lack of demand for the product and increased security measures. Hackers who try to get accounting data of their victims are mostly forced to use social engineering methods, which requires a lot of effort with a relatively low level of success.
MALWARE
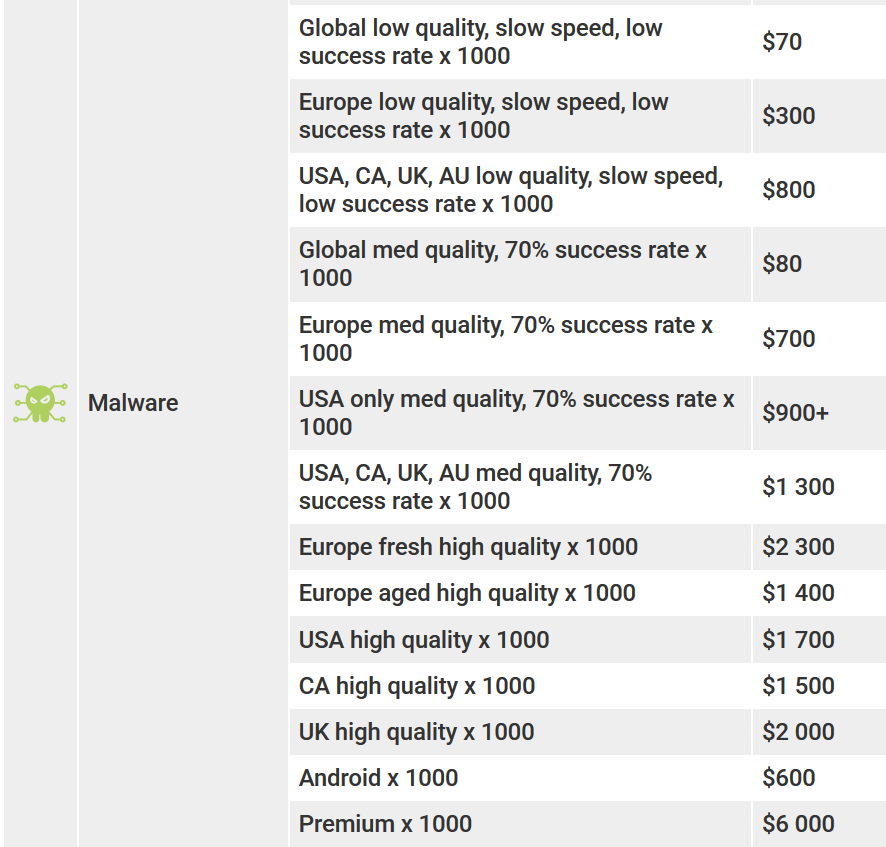
Malicious programs can be installed on compromised systems (Windows, Android, etc.), allowing attackers to access the system. The initial installation is carried out via online gambling, FB/social networks, pirate sites, etc.
Some types of malware can use your computer’s resources for operations such as cryptographic mapping. Others can be used to steal your credentials when you enter them on a website. For every 1000 installations, hackers often get tens of thousands of dollars.
DDoS ATTACKS

The Denial of Service (DDoS) attack aims to disable a website by sending thousands of requests per second to overload the website server and cause it to fail.
WHY THIS INFORMATION IS SO IMPORTANT
People usually do not need data from the illegal market, as they most likely do not look for stolen payment card data or PayPal accounts.
If someone gets to your financial information or social media credentials by paying the price listed above, it will fully pay off. That will likely be much more valuable to you than to the cybercriminals. They think of you like about another victim for quick earning.
You can protect your data from scammers with a couple of simple rules and habits. With this knowledge, it is a mistake not to use it to protect your data.
However, there is nothing reliable – we are all already hacked by default, following the principle of zero trust. So anyone can steal your data whenever and wherever wants. But! You can make it very difficult for criminals, thus increasing their labor costs and reducing interest in your information.
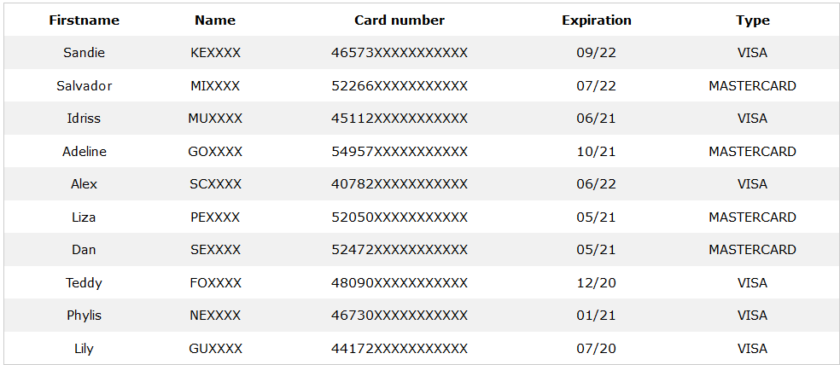
An example of what stolen credit card data is.
If the card data were stolen, you could go to your bank to recover and restore most of the assets, but this is a long process and a big headache. There may also be other consequences, such as an unexpected loan on your name, which may take years to restructure.
HOW TO PROTECT YOURSELF FROM IDENTITY THEFT
- Never give out confidential information over the phone: (bank card number, passwords) to anyone, regardless of whether it is a requirement for any process. If it is so important, do it in person.
- Whenever you use an ATM, there is a risk that there is a skimmer, keyboard overlay, or an extra camera on the ATM panel.
Skimmers read the card as soon as you put it in, creating a clone of your card. That’s enough to recreate your card from scratch.
The pad on the keyboard reads your PIN code. It works in conjunction with a device installed inside the ATM, which blocks the card in the ATM. The keyboard remembers the typed PIN-code.
An additional camera on the ATM panel. It can have a variety of shapes, sometimes just black glass circles. The camera installed with the same purpose as the keyboard pad – it remembers the typed code.
So it is better to use ATMs, which are directly in the banks.
- Regularly update your antivirus software.
- Avoid public or unprotected Wi-Fi networks. If you need to log into your account on a network that you do not trust 100%, use a VPN to encrypt all connections. Even bank sites can be faked in ways that are almost impossible to recognize if an attacker has administrative access to the network you are using.
- Remove accounts that you no longer use. Old accounts could be compromised, and this could lead to problems in the future. Furthermore, this problem can get worse if you use the same password for multiple accounts.
- Never use the same password for more than one account. That is the easiest way for an attacker to gain access. When the main list of account details gets to the DarkNet, your account details can be compared with your details in other services such as email, banking, etc.
- Use a password manager such as LastPass or Keepass (both free), and you will always have strong security for all your accounts. You will only need to remember one master password.
These rules may seem complicated and time-consuming, but once you get used to following them, they’ll be as natural and vital to you as brushing your teeth and washing your hands. In this way, you develop a “sense” of cybersecurity both in digital environments and in everyday life.
Source: PrivacyAffairs